Sign up for future insights
No spam. Just the latest market insights by Seguro in your inbox each week.
The Importance Of Safe Manual Handling In Your Business
All manual work involves lifting and handling to some extent. Although mechanical equipment should be used whenever practicable, much of the work will inevitably continue to be done manually. The risk of injury can be greatly reduced by a knowledge and application of correct lifting and handling techniques and by taking a few elementary precautions.
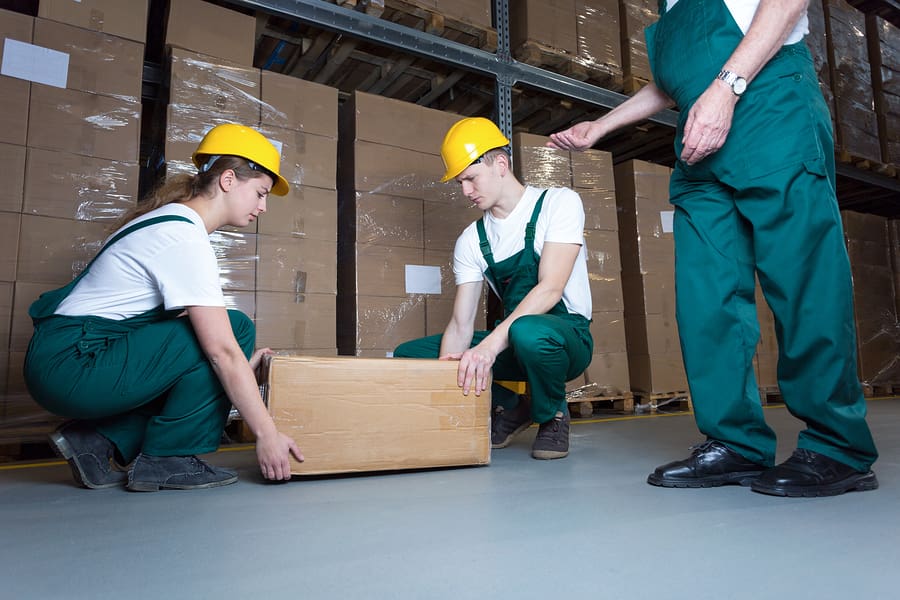
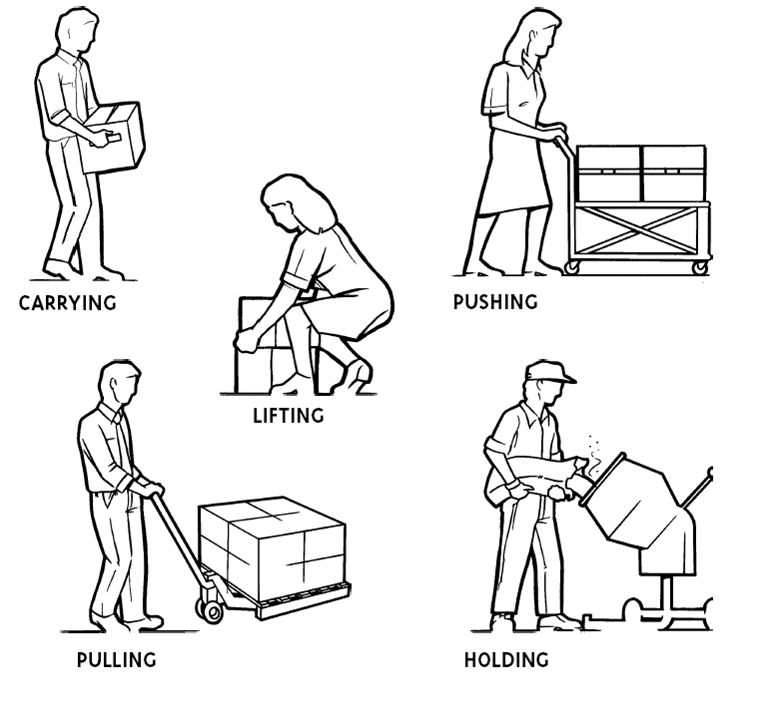
Manual handling relates to transporting or supporting of a load (including lifting, putting down, pushing, pulling, carrying or moving thereof) by hand or by bodily force” It is the most common recognised reason for injury at work.
In any case, it’s not simply ‘pulling something’ because of the heaviness of an item, injuries can be brought on in different causes, for example:
- Reaching and lifting over your head
- Long carrying distances
- Twisting
- Bending
- Any poor stance positions
- Lifting or carrying objects with awkward or odd shapes
Over 20% of all accidents occurring in the UK Construction Industry each year involve injuries sustained whilst manually lifting and handling materials or equipment. This incorporates Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs), e.g. injuries or pain in the body’s joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons, and structures that support limbs, neck and back. Manual handling injuries can happen anyplace inside of the working environment; However, manual labour, existing injuries and unbalanced stance positions can increase the risks.
Manual handling can have consequential implications for the employer and for the individual who has been injured. The employer may bring about some significant expenses, for example, sickness payment, lost production, retraining of a brief labourer, over time to cover the absence and, possibly, compensation. The injured individual may find that their capacity to carry out their occupation has been influenced and their way of life may need to change.
In this manner, it is basic that you must consider the risks and where there are risks, regulations apply.
The Regulations establish a clear hierarchy of measures:
- AVOID handling operations involving risk of injury
- ASSESS operations involving risk of injury that cannot be avoided
- REDUCE the risk of injury e.g. using handling aids and provide information on the load
- REVIEW the assessment
Employers Duties
- Carry out a Manual Handling Assessment
- Reduce risk of injury
- Replace Manual tasks where possible
- Introduce mechanical aids
Employees likewise have responsibilities:
- Make proper use of equipment & follow safe working systems
- Co-operate with their employer
- Ensure others are not put at risk
- Avoid tasks likely to cause injury
- Co-operate with the employer to reduce the risk of injury to themselves and others
There are numerous routes in which manual handling can be maintained, see the HSE’s brief guide on manual handling.
Share this post
Copy link