Outsource Health and Safety
Outsource health and safety and make your life a lot easier.
The pros of outsourcing definitely outweigh the cons, but before you form a partnership with a Health & Safety consultant, you must learn all you can about outsourcing. Once you are fully informed, you can decide if outsourcing is right for your business and how it can help you.
Following is a list of pros and cons of outsourcing:
Pros of Outsourcing
- Up-to-date professional advice when you need it
- Gives you access to skilled professionals at a low cost
- The confidence in knowing your legal duties are covered
- Reduces your cost of doing business, as you save on infrastructure, workforce, hiring costs, training costs, and technology and software investments
- Allows you to focus more on your core business functions
Cons of Outsourcing
- You will have to rely on the expertise of another company without fully understanding all the detail yourself
- You need to ensure that your outsource partner is available for your working hours, not just theirs
- You need to understand turn around times and accept them
- You may not be able to get what you want when you want it
- You have to trust the information they provide is accurate and up-to-date
Outsourcing your Health & Safety resources can give your business the competitive edge it requires to win work and be successful on tenders.
If anything, the disadvantages of outsourcing give you the opportunity to think before-hand about the things you need to keep in mind when selecting an outsourcing partner.
Seguro Health and Safety Advisor Service
Here at Seguro, we pride ourselves on being able to support all businesses regardless of their size. We can provide your business with less than five employees a service, ensuring you meet all your Health & Safety needs.
Our service provides you with:
- Support to implement new documentation into your business
- Provide support ongoing should you need it for all Health & Safety advice.
- Provide off-the-shelf risk assessments and method statements should they be needed (bespoke ones are chargeable)
- Enable you to name us should you need to on PQQ documentation
- Provide you with General pre-prepared COSHH from our library
We are available throughout the working day by email or telephone, whichever way you prefer to communicate.
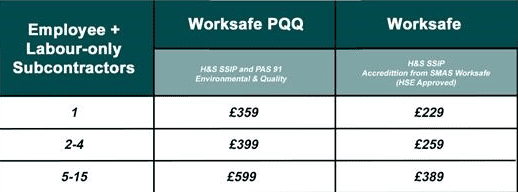
This service is available to anyone who needs it, and there is a fixed cost for everyone.
This service is also FREE with any accreditation we submit for you so if you are looking to get CHAS or a similar SSIP we can assist with that and provide this service for FREE.
If you need more information about SSIP, we have lots of blogs to help or you can visit SSIP directly.
Included in our safety advisor service
- Put Seguro down as your named health & safety advisor.
- Use our name when filling out pre-tender qualification questionnaires.
- Use a CV from one of our Consultants.
- We are here as back-up should you require advice and guidance on health & safety issues.
Outsource Health and Safety Support
Complete the form, and we will get in touch and give you free advice and direction on outsourcing your health and safety.